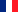
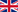
Background
Herniated lumbar intervertebral discs are cartilaginous plates surrounded by a fibrous ring which lie between the vertebrae and serve to cushion. For, wear and tear or trauma, the fibrous tissue (annulus) that surrounds the soft disc material (nucleus pulposus) may tear. This causes the disc protrusion or extrusion of disc material into the canal or neural foramen. This has been called herniated discs, ruptured discs, nucleus pulposus, or prolapsed disc.
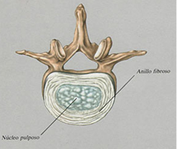
This disc herniation may become significant if a nerve root is compressed. The irritation of a nerve root causes pain along the nerve, typically the back of the leg, one side of the calf and possibly to one side of the foot.
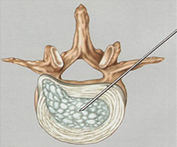 If you are sensory function of the nerve root involved, there might be insensitive. The exact sensitivity is lost deteminada by the particular root, and may be the inner ankle, the toe, heel, the outer ankle, the outer leg, or a combination thereof. If you are involved in motor function of the root will cause weakness which again depends on the particular root, and may include weakness or collapse the stretch to lift the ankle or toe.
If you are sensory function of the nerve root involved, there might be insensitive. The exact sensitivity is lost deteminada by the particular root, and may be the inner ankle, the toe, heel, the outer ankle, the outer leg, or a combination thereof. If you are involved in motor function of the root will cause weakness which again depends on the particular root, and may include weakness or collapse the stretch to lift the ankle or toe.
| Manifestación | Nivel de Herniamiento Discal | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| L3-L4 | L4-L5 | L5-S1 | |
| Raíz Comprimida | L4 | L5 | S1 |
| Debilidad | cuadriceps, tibia anterior | extension del dedo gordo | flexion del tobillo |
| Implicación del Reflejo | movimiento brusco rodilla | no significativa | tendón de Aquiles |
| Pérdida Sensorial | tobillo medio | dedo gordo | lado del pie y talón |
| Distribución del Dolor | parte delantera muslo | parte trasera muslo | parte trasera muslo, lateral pantorrilla |
Table. The most common clinical manifestations of lumbar disc herniation. (Spanish).
Table summarizes the main sídromes of lumbar disc herniation. Note that the L5-S1 disk is involved in 45-50% of cases, L4-L5 40-45%, and L3-L4 about 5%. Disc herniation at other lumbar levels is rare. The root compressed is the one below in most cases. However, if the herniation is lateral, into the hole, the compressed root is the one above. This type of hernia is rare and occurs in 3-10% of cases. It is also important to note that although signs are helpful in diagnosis and determining the type of treatment could not be present all the symptoms related to a particular root, and still be symptoms related to multiple roots.
Diagnosis.
The diagnosis should be suspected from clinical history and physical examination. Radiographic studies should be done to make the diagnosis and define the location and configuration. Generally prefer a magnetic resonance imaging and non-invasive (no need to use needles or injections) and provides excellent detail. The CT scan, while inferior to MRI concerning soft tissue detail is superior bone detail, and is faster and cheaper. For this reason, a CT scan is good enough to diagnose a herniated lumbar disc that has no complications. Computed tomography has long been the gold standard because of its excellent definition of the spaces around the nerve roots. The disadvantage is that it requires injection of contrast dye through a lumbar puncture. He has often been supplanted by MRI, but should be considered as a complementary rather than as an alternative, and in many cases is essential.