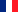
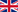
Clinical aspect
In herniated lumbar spine intervertebral disc herniation is a Cando often found weakness in the fibrous ring that surrounds the disk, whereas in the lumbar nerve roots are only at the level of the cervical spine cervical spinal cord there and this can also be compressed by the herniated disk.
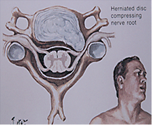
The signs and symptoms caused by a herniated disk herniation depend if compress a nerve root, whether directly compresses the spinal cord compression, or both at the time.
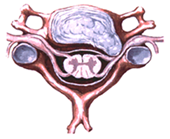 The most common complaint is neck pain which restricts movement and is aggravated by neck extension. The pain may also spread to one arm, in a characteristic pattern of the particular root involved (see below). Patients often hold the arm elevated and behind the head, presumably because this maneuver reduces stress on the nerve root and lessens the pain. In many cases, the onset of pain is upon waking, without there having been no trauma or event that caused.
The most common complaint is neck pain which restricts movement and is aggravated by neck extension. The pain may also spread to one arm, in a characteristic pattern of the particular root involved (see below). Patients often hold the arm elevated and behind the head, presumably because this maneuver reduces stress on the nerve root and lessens the pain. In many cases, the onset of pain is upon waking, without there having been no trauma or event that caused.
| Manifestación | Nivel de Herniamiento Discal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4-L5 | C5-C6 | C6-7 | C7-T1 | |
| Raíz Comprimida | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 |
| Debilidad | deltoides | bíceps | tríceps, extensión de la muñeca | inherente a la mano, flexión de la muñeca |
| Pérdida de sensibilidad | hombro lateral | lateral brazo y antebrazo, pulgar y lateral del dedo indice | dedo medio | dedos anular y meñique |
| Implicación de los reflejos | deltoides, pectorales | bíceps | tríceps | flexión de los dedos |
Table. The most common clinical manifestations of cervical disk herniation. (Spanish).
The Table shows the usual syndromes (radiculopathy) from cervical root. Note that the disc C6-7 is the most commonly herniated, about 2 / 3 of cervical herniation. The C5-L6 disc is involved in about 20% of cases, the C7-T1 about 10% and the C4-C5 about 2%.
If the disc herniation compresses the spinal cord, certain defects may occur (myelopathy). The weakness in hands and arms can be generalized or bilateral rather than confined to a distribution of root. Moreover, it is weakness in the legs, usually manifested initially by a feeling of heaviness in the legs and difficulty walking considerable distances or up stairs. Neurological examination may show hyperactive reflexes, pathological reflexes and "spasmodic gait (spastic gait). Finally, the sphincter and sexual function may be compromised, usually in the progression of myelopathy.
Lhermitte's sign refers to a sudden electrical sensation down the neck and back, caused by neck flexion. It was originally described by a patient with multiple sclerosis and dorsal column dysfunction. The conditions that can produce symptoms of Lhermitte are:
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Cervical spondylosis.
- Cervical disc herniation.
- Cervical spinal cord tumor.
- Chiari I malformation
- Radiation myelopathy.
- Subacute combined degeneration (caused by vitamin B12 deficiency).
Other symptoms can help determine the diagnosis. They suggest a herniated disc much when present, yet are often absent in the presence of the disease (ie, are specific but not sensitive). Spurling's sign refers to the reproduction or exacerbation of pain by pressing the head down and bending toward the affected side. Pain reduction by applying axial traction to the head also suggests a hernia. Finally on the shoulder abduction test, whether to lift the affected arm above the head reduces the pain.